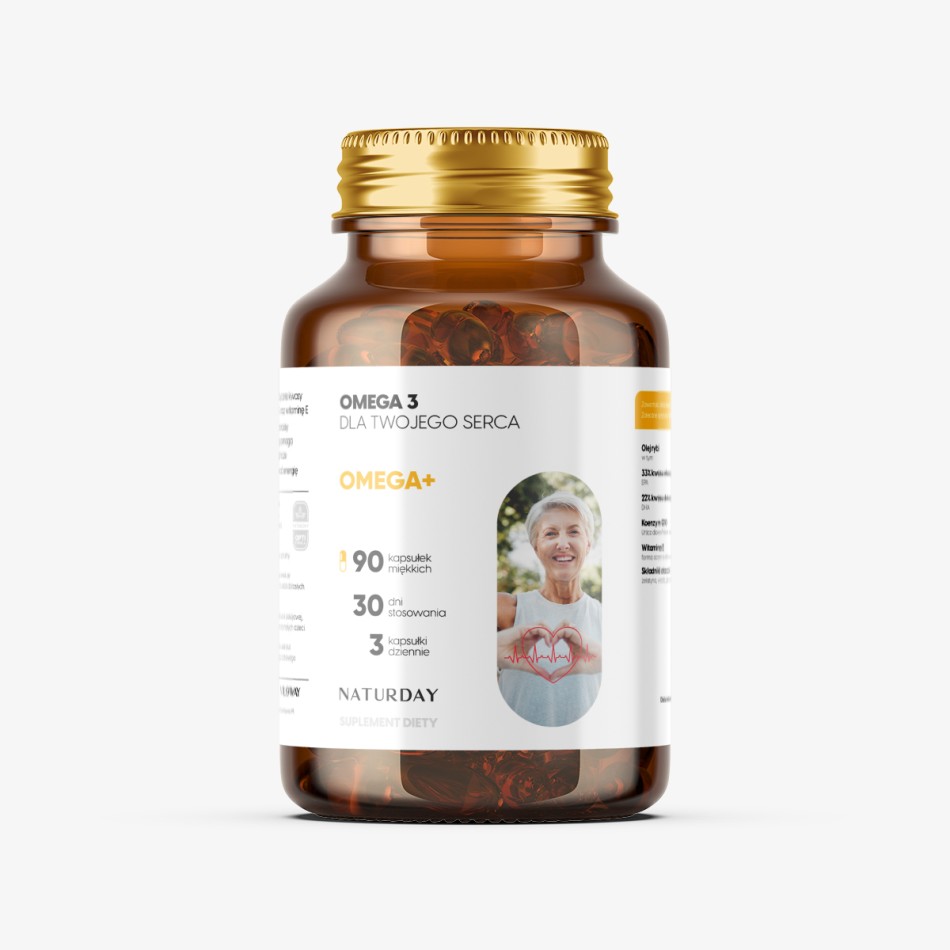
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, play a vital role in the proper functioning of the human body. Since our bodies cannot produce these essential fatty acids in sufficient quantities, they must be obtained through diet or supplementation.
EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) is especially known for its cardiovascular benefits. Scientific studies indicate that EPA can help reduce blood triglyceride levels and support normal heart function. Additionally, EPA plays an important role in regulating inflammatory processes in the body.
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) makes up approximately 40% of the polyunsaturated fatty acids in the brain and 60% in the retina. DHA is essential for the proper development and functioning of the nervous system, contributing to cognitive performance, memory and concentration.
Coenzyme Q10 is a naturally occurring compound in the body that plays a key role in cellular energy production. As we age, endogenous levels of Coenzyme Q10 decline, potentially reducing the energy efficiency of cells - especially those with high energy demands, such as heart and brain cells.
Vitamin E in the form of d-alpha-tocopheryl acetate is a natural antioxidant that protects delicate omega-3 fatty acids from oxidation, ensuring their stability and bioavailability.
It’s worth noting that modern diets are often low in omega-3 fatty acids, especially among individuals who consume little to no fatty fish. Supplementation can be a valuable addition to the diet - particularly for individuals over the age of 40, when natural Coenzyme Q10 synthesis begins to decline.