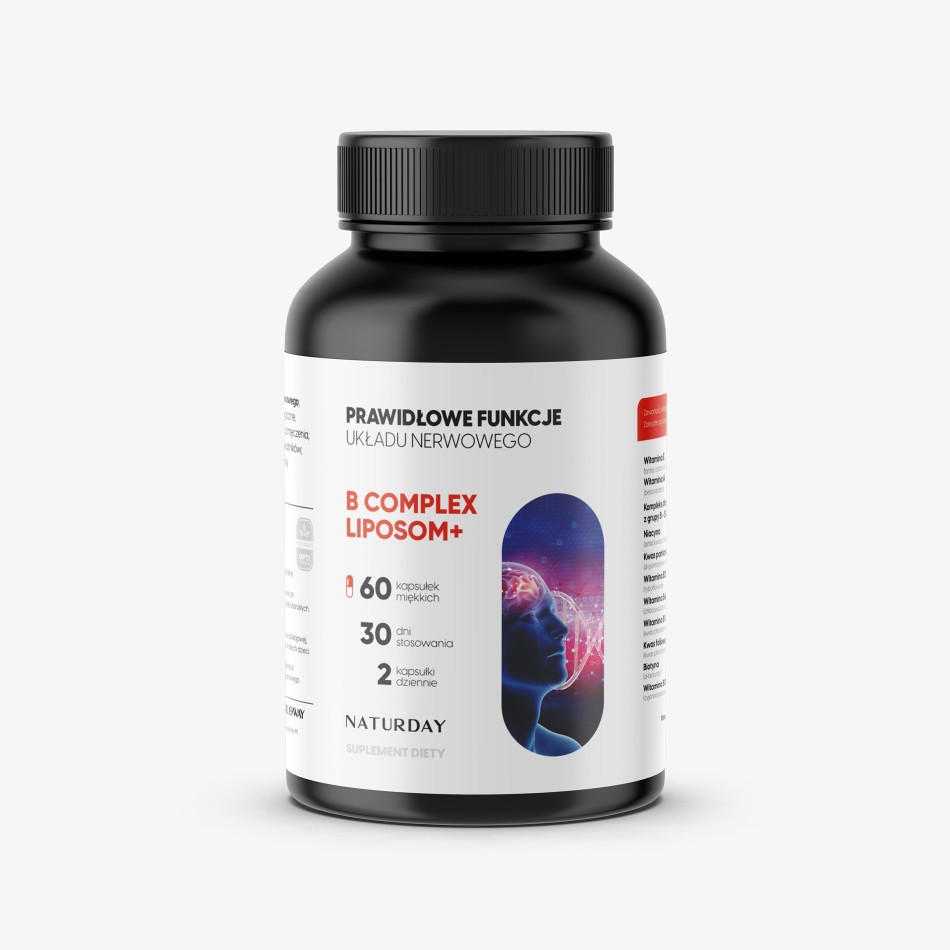
B Complex Liposom+ is a breakthrough B vitamin formula based on advanced liposomal technology, revolutionizing the way active ingredients are absorbed by the body. Soy-derived phospholipids form natural liposomes - microscopic delivery vehicles that transport vitamins directly to the cells, increasing their bioavailability by up to 90% compared to traditional forms.
The highlight of this complex is a precisely formulated matrix of B vitamins - B1, B2, B6, B12, niacin, pantothenic acid, biotin, and folic acid, which supports key metabolic processes in the body. Vitamin E acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting B vitamins from oxidation, while vitamin A supports cellular regeneration and proper immune function.
This unique combination of ingredients within a phospholipid liposomal shell ensures optimal absorption and sustained release of active compounds, resulting in maximum supplement effectiveness.




































_1_780px.png)