- 100% natural formula - sugar free, without artificial colors, fillers and palm oil. A composition which supports the healthy development of all children.
- Pectin instead of gelatin ensures safety and is suitable for vegetarians - no risk of diseases associated with gelatin of animal origin.
- Contains 15 key vitamins and minerals, including inositol and choline, which support brain development, which is crucial for children in the phase of intensive growth.
- for children over 3 years of age
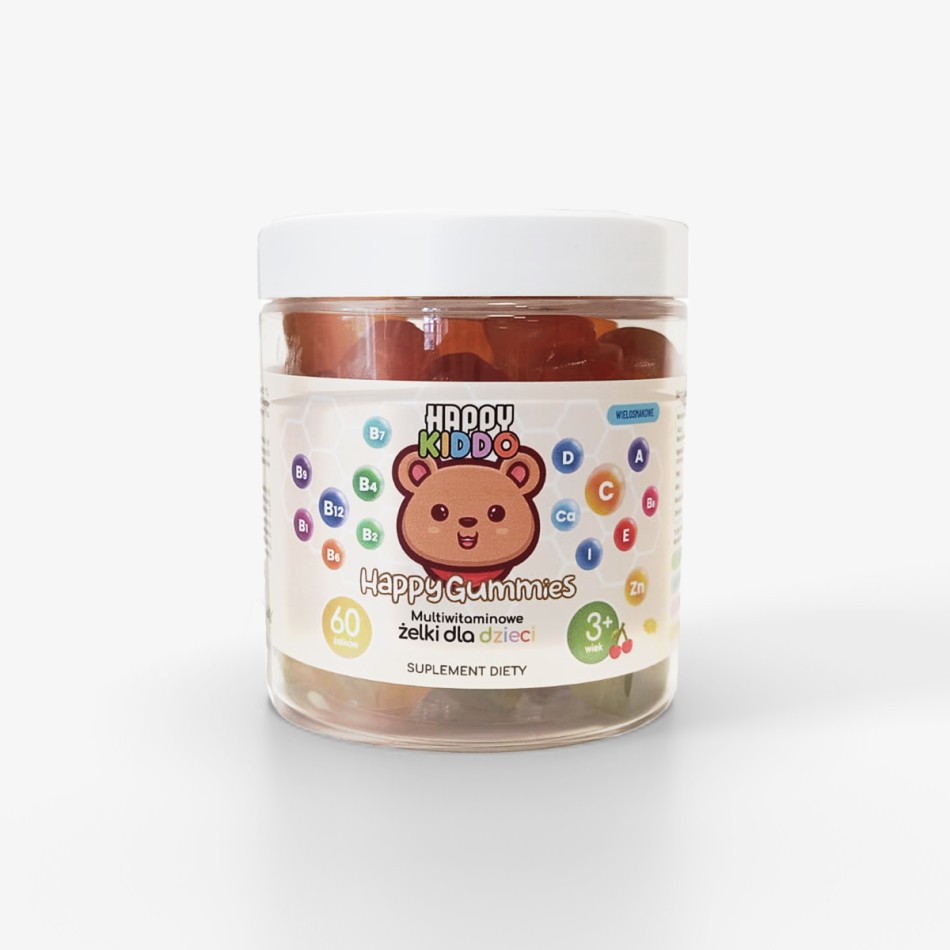

Dear Parent, it was important for us to create a product with a 100% natural formula, free from sugar, artificial colors and palm oil. Our supplement supports children by taking care of their sensitive nervous system and immunity. Thanks to pectin, instead of gelatin, it is safe and suitable for vegetarians.
It contains 15 key vitamins and minerals, including inositol and choline, which support brain development. Ideal for children over 3 years old, it supports immunity, healthy growth, and the development of bones and teeth. It’s a convenient and appealing way to supplement your child's diet.
Take 2 jellies / a day as a dietary supplement.
Nutritional value / 100g:
Energy value - 35 kJ / 8.4 kcal
Fat - 0.5 g
Unsaturated fatty acids - 0.4 g
Carbohydrates - 0.86 g
of which sugars - 0 g
Polyols - 0 g
Protein - 0 g
Dietary fiber - 2.2 g
Sodium chloride - 0 g
Content of ingredients in a daily serving - 2 gummies daily:
Vitamin C - 40 mg (50% NRV*)
Choline - 10 mg
Zinc - 8 mg (80% NRV*)
Vitamin E - 6 mg (50% NRV*)
Calcium - 2.5 mg (32% NRV*)
Vitamin B6 - 1 mg (71.4% NRV*)
Vitamin B2 - 0.85 mg (61% NRV*)
Vitamin B1 - 0.70 mg (64% NRV*)
Vitamin A - 0.45 mg (50% NRV*)
Folic acid - 0.10 mg (50% NRV*)
Iodine - 0.05 mg (30% NRV*)
Vitamin D3 - 0.03 mg (500% NRV*)
Biotin - 0.02 mg (30% NRV*)
Inositol - 0.01 mg
Vitamin B12 - 2.5 μg (100% NRV*)
*NRV - Nutrient Reference Value
Store at room temperature, out of the reach of small children.
Do not use in children under 3 years of age.
Happy Gummies
is for you if:
- You want to avoid sugar and artificial additives in your child's diet, minimizing the risk of metabolic disorders and impulsive behavior.
- You are looking for an alternative to products with gelatin, which may put your child's health at risk.
- You want to support the proper development of the child's brain and entire nervous system thanks to the presence of inositol and choline.
- You want to strengthen your child's immunity by providing him with a complex of vitamins and minerals in an easy-to-take form.
- You are interested in natural support for the health of your child's bones and teeth through supplementation with calcium and vitamin D3.
- You are looking for a supplement whose ingredients support the healthy growth and development of your child thanks to the balance of B vitamins, vitamin A, C and E.
- You need a convenient and attractive way to supplement your child's diet with essential nutrients that support their active lifestyle and learning.
What do our recipients say about Happy Gummies?
Do you have Happy Gummies?
Describe your experience with the product, add a review and help others choose.
I can finally provide my children with the vitamins they need without a fight - the kids love the taste and treat them like a treat! In addition, I'm glad that they are natural and without unnecessary artificial additives, so I can be sure that I'm taking care of their health in the best possible way.
I can finally provide my children with the vitamins they need without a fight - the kids love the taste and treat them like a treat! In addition, I'm glad that they are natural and without unnecessary artificial additives, so I can be sure that I'm taking care of their health in the best possible way.

The power of vitamins locked in gummies for children and not only, the effect is incomparable to other preparations for immunity
The power of vitamins locked in gummies for children and not only, the effect is incomparable to other preparations for immunity

The kids love them, they are delicious! Brilliant composition
The kids love them, they are delicious! Brilliant composition

Jellybeans that cause me joy at the level of so many vitamins, high composition , without sugar that supports my children in the functioning of the small body, although I admit that I also snack
Jellybeans that cause me joy at the level of so many vitamins, high composition , without sugar that supports my children in the functioning of the small body, although I admit that I also snack

Great product, knock on wood, we've been using for several months and we're doing without gil and sickness.
Great product, knock on wood, we've been using for several months and we're doing without gil and sickness.

My daughter was often sick, since I use jellybeans,you can see the difference. On top of that, she readily reaches for them. Unlike others. Always available in our house.
My daughter was often sick, since I use jellybeans,you can see the difference. On top of that, she readily reaches for them. Unlike others. Always available in our house.

Jellybeans that cause joy in my family. My kids like them a lot and I love them for the properties and composition because I know they are getting a full set of vitamins👌.
Jellybeans that cause joy in my family. My kids like them a lot and I love them for the properties and composition because I know they are getting a full set of vitamins👌.

Very good composition of the product, the children liked the jelly and I know that I have chosen the best product for my children.
Very good composition of the product, the children liked the jelly and I know that I have chosen the best product for my children.

Do you have any questions?
You are supported by our service office and experts.
From Monday to Friday 8:00 - 16:00.